Data Types
Hongtu supports the following data types:
BooleanNumberStringObjectArrayAny
As Hongtu is a visual programming language, we assign a unique visual representation to each type of data. For handles with different data types, the color of the handle is different, and usually cannot be connected, unless:
- if the source type can be converted to the target type, implicitly
- if the target is
Array, single or array of the same type can be connected - when target is of type
Any
Boolean
Boolean data is in dark red. They can be used to represent true or false. Some examples are:
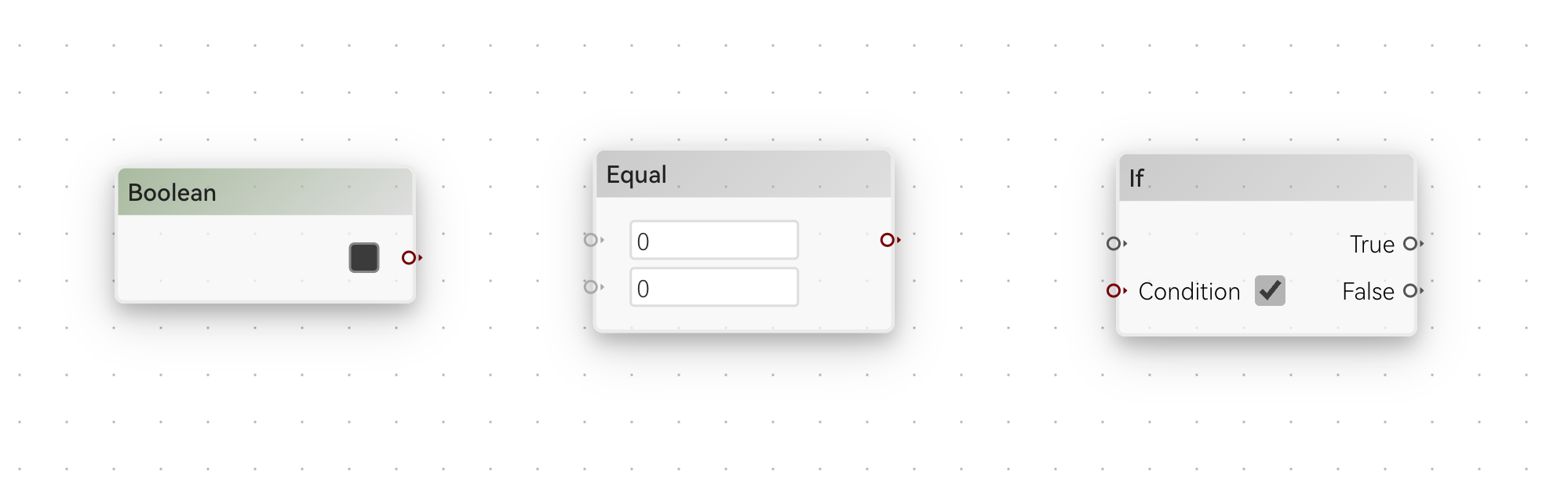
See the handle of each node that either produce or consume a Boolean data.
Number
Number data is in green. They can be used to represent numeric values. Some examples are:
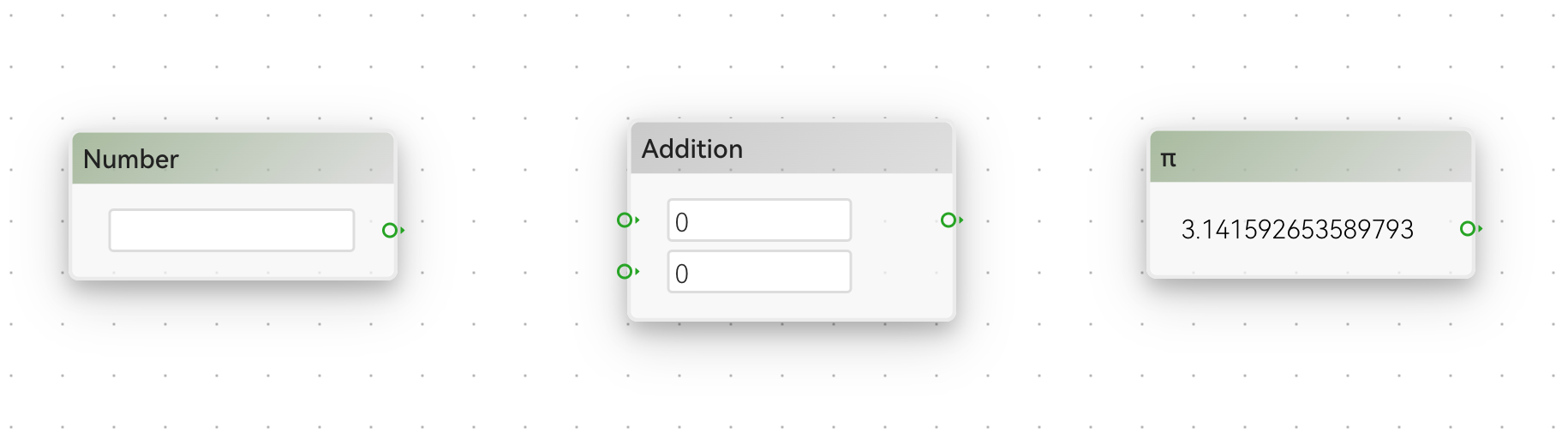
String
String data is in purple. They can be used to represent text. Some examples are:
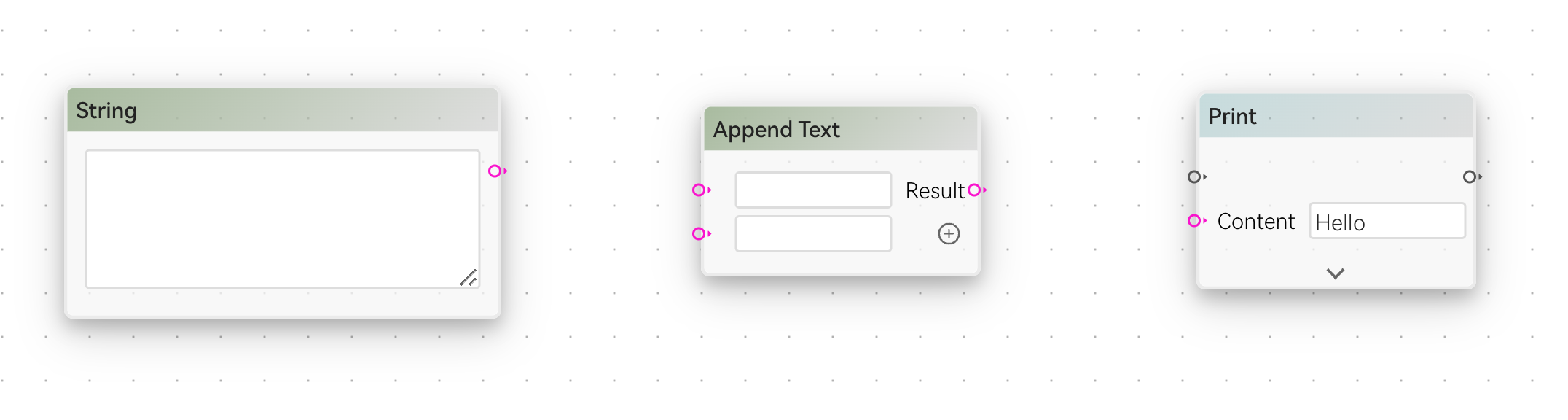
Object
Object data is in blue. Boolean, Number, String are called primitives in many programming languages. They are the simplest data types. Object, is a combination of these primitives, and can be used to represent complex data. Some examples are:
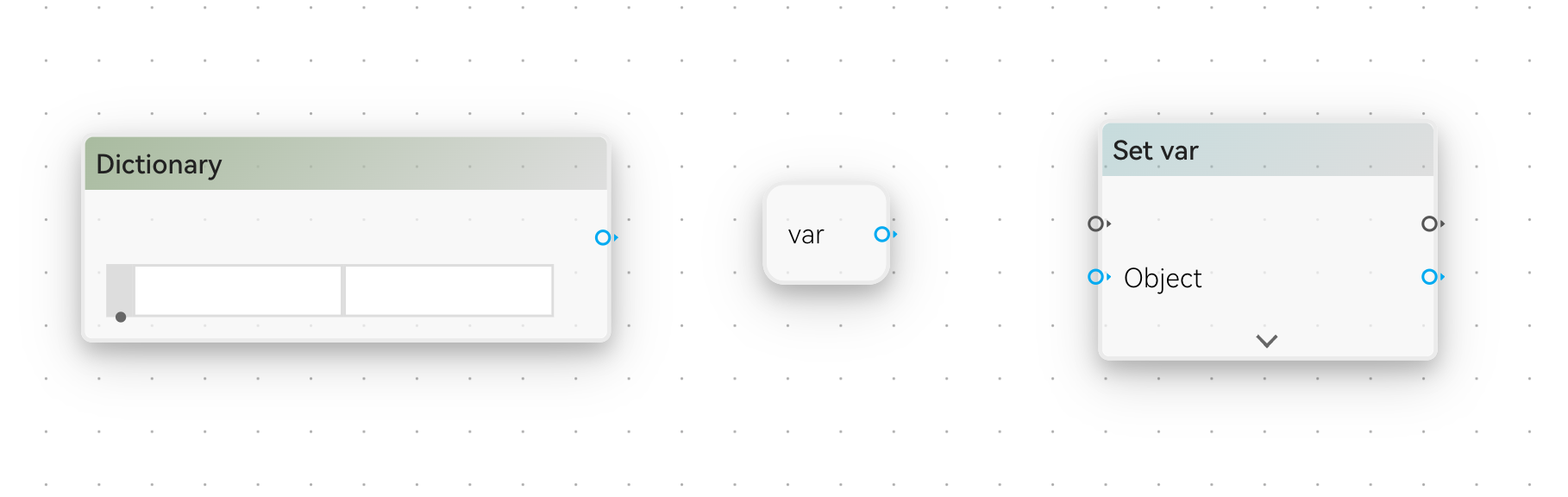
Array
The color of an array is the same as the color of the element in that array. However, instead of Solid circle, Array has a Dashed circle. For example:

One interesting thing about Array is that when it acts as a target, it can accept any combination of single or array with the same type, so for example:
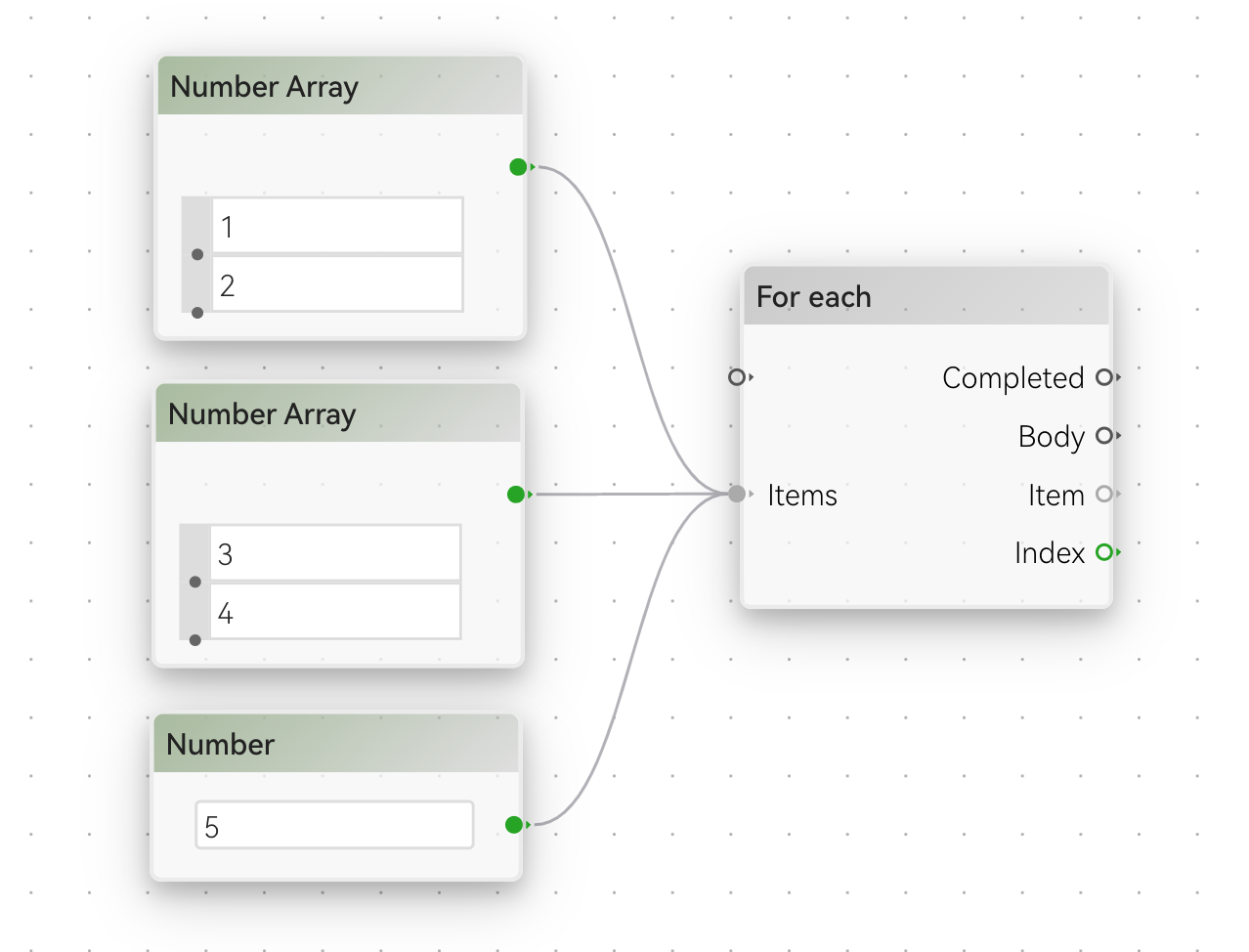
The For each node will iterate through all the data connected to Items handle, which accepts an Array of Any, so you can add any combination of single or array values.
Order of Iteration
The nodes that are on the upper part of the screen will be iterated first. So to change the order of iteration, drag the nodes up and down.
Any
Any is in gray. It can be used to store any data type.